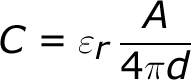A semiconductor diode that emits light when current flow through it. When electrons in semiconductor recombine with electron wholes than an energy release in form of photon. Light emitting diodes emit either visible light or invisible infrared light when forward biased. The LEDs which emit invisible infrared light are used for remote controls.
LEDs
A diagram of the inside of an LED is shown in Figure The chip at the heart of the LED
consists of a p-n junction --- two different solid materials that have been joined together. It
is surrounded by a transparent, hard plastic that protects the LED from vibration and shock.
The LED is constructed in such a way that the light emitted by the chip is reflected off the
base it sits on and is focused through the top of the LED. Thus, the light is brightest at the top of LED.
p-n junctions
A solid can be a pure material in which all atoms are the same element. As a result, each
nucleus of the atom contained in this solid has the same electrical charge. Thus, each atom
in this solid has identical properties. The interactions among these atoms create the energy
bands and gaps that we have studied. Modern technology can create materials that are
very close to being all identical atoms. These pure materials have light emitting properties
much like we have studied here.
For today’s technology pure materials are not the most valuable. Instead, a wide range of
devices — from LEDs to computer chips — use almost pure materials into which an impu-
rity has been introduced. Then materials with different impurities are joined.
Suppose we start with a pure material and add atoms of a different element. These differ-
ent elements will have a different number of electrons than the atoms of the original mate-
rial. We place the impurities into two groups:
• Donors, or n-type, have more electrons than the material’s pure elements. They donate electrons to the solid.
• Acceptors, or p-type, have fewer electrons than the material’s pure element. They
accept electrons from the solid.
Both the donors and acceptors have zero electrical charge. They have more or less charge
in the nucleus to balance the more or fewer electrons.
The LED chip consists of two solids – a material that has been supplied with donor atoms
and the same material that has been supplied with acceptor atoms. The combination is the called p-n junctions.
Layers of LED
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) consists of three layers: p-type semiconductor, n-type semiconductor and depletion layer. The p-type semiconductor and the n-type semiconductor are separated by a depletion region or depletion layer.
P-type semiconductor
When trivalent impurities are added to the intrinsic or pure semiconductor, a p-type semiconductor is formed.
In p-type semiconductor, holes are the majority charge carriers and free electrons are the minority charge carriers. Thus, holes carry most of the electric current in p-type semiconductor.
N-type semiconductor
When pentavalent impurities are added to the intrinsic semiconductor, an n-type semiconductor is formed.
In n-type semiconductor, free electrons are the majority charge carriers and holes are the minority charge carriers. Thus, free electrons carry most of the electric current in n-type semiconductor.
Depletion layer or region
Depletion region is a region present between the p-type and n-type semiconductor where no mobile charge carriers (free electrons and holes) are present. This region acts as barrier to the electric current. It opposes flow of electrons from n-type semiconductor and flow of holes from p-type semiconductor.
To overcome the barrier of depletion layer, we need to apply voltage which is greater than the barrier potential of depletion layer.
If the applied voltage is greater than the barrier potential of the depletion layer, the electric current starts flowing.
How Light Emitting Diode (LED) works?
Light Emitting Diode (LED) works only in forward bias condition. When Light Emitting Diode (LED) is forward biased, the free electrons from n-side and the holes from p-side are pushed towards the junction.
When free electrons reach the junction or depletion region, some of the free electrons recombine with the holes in the positive ions. We know that positive ions have less number of electrons than protons. Therefore, they are ready to accept electrons. Thus, free electrons recombine with holes in the depletion region. In the similar way, holes from p-side recombine with electrons in the depletion region.
Because of the recombination of free electrons and holes in the depletion region, the width of depletion region decreases. As a result, more charge carriers will cross the p-n junction.
Some of the charge carriers from p-side and n-side will cross the p-n junction before they recombine in the depletion region. For example, some free electrons from n-type semiconductor cross the p-n junction and recombines with holes in p-type semiconductor. In the similar way, holes from p-type semiconductor cross the p-n junction and recombines with free electrons in the n-type semiconductor.
Thus, recombination takes place in depletion region as well as in p-type and n-type semiconductor.
The free electrons in the conduction band releases energy in the form of light before they recombine with holes in the valence band.
In silicon and germanium diodes, most of the energy is released in the form of heat and emitted light is too small.
However, in materials like gallium arsenide and gallium phosphide the emitted photons have sufficient energy to produce intense visible light
Symbol of LED